Throughout history, art has served as a profound testament to human creativity, with masterpieces that continue to resonate across generations.
From Renaissance masters to modern visionaries, these historical artists shaped entire movements and inspired generations of creators.
For anyone curious about the brilliant minds behind great works like the Mona Lisa or Starry Night, understanding the most famous artists offers insight into both cultural shift and creative genius.
These art figures offer valuable insights into creativity, perseverance, and the power of art. So, let’s get into it!
How Great Artists Shaped Civilization?
The most famous artists throughout history have significantly influenced society beyond their canvases. Historical artists like Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci changed art to new heights during the Renaissance.
Later, impressionists challenged traditional standards, while modern artists like Picasso redefined visual language itself.
These artists didn’t simply create beautiful works, but they also sparked cultural movements, documented pivotal moments, and gave voice to societal changes.
Their contributions extend into architecture, literature, fashion, and design as well.
The Renaissance Masters
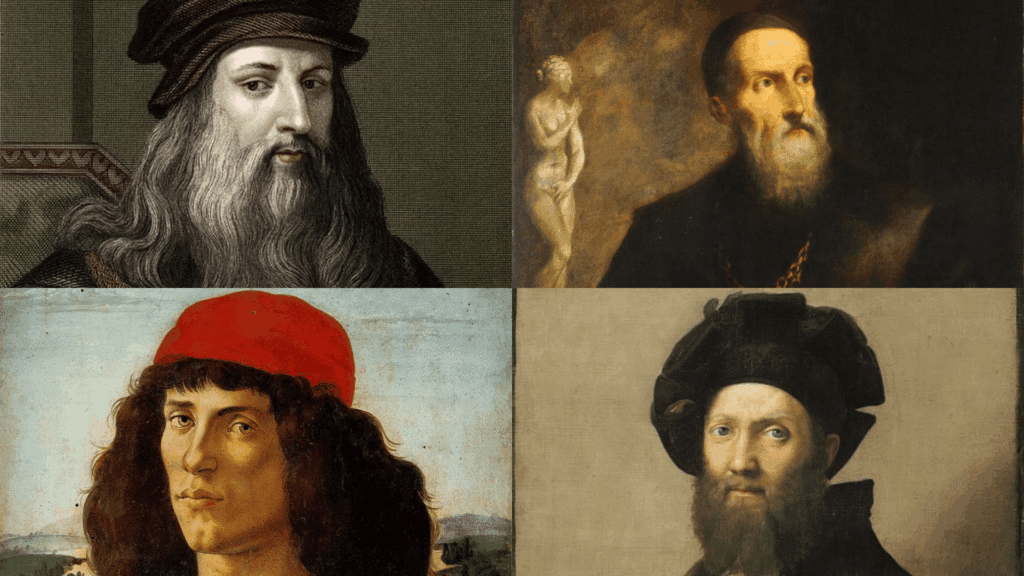
The Renaissance marked a cultural rebirth that changed European art through humanism and classical revival.
These famous artists in history developed techniques such as linear perspective, which established the foundations of Western painting.
1. Leonardo da Vinci
The Renaissance polymath combined scientific inquiry with artistic mastery, creating works that bridged art and anatomy.
His meticulous studies of human proportion and natural phenomena revolutionized painting techniques and established new standards for realism.
- Lifespan: 1452–1519
- Nationality: Italian (Florentine)
- Styles and Themes: High Renaissance, sfumato technique, human anatomy, scientific observation
- Known For: Mona Lisa, The Last Supper, Vitruvian Man, anatomical drawings, engineering inventions
2. Michelangelo
He is one of the most famous artists in history, a sculptor, painter, and architect whose powerful depictions of the human form defined Renaissance ideals of beauty and strength.
His ceiling frescoes in the Sistine Chapel are among humanity’s greatest artistic achievements.
- Lifespan: 1475–1564
- Nationality: Italian (Florentine)
- Styles and Themes: High Renaissance, muscular figures, biblical narratives, humanism, dramatic tension
- Known For: Sistine Chapel ceiling, David sculpture, Pietà, The Creation of Adam, The Last Judgment
3. Raphael
Renowned for harmonious compositions and graceful figures that epitomized Renaissance balance and beauty.
His Madonna paintings and grand frescoes in the Vatican demonstrated a perfect synthesis of classical ideals with contemporary religious devotion.
- Lifespan: 1483–1520
- Nationality: Italian (Urbino)
- Styles and Themes: High Renaissance, classical harmony, balanced composition, Madonnas, portraiture
- Known For: The School of Athens, Sistine Madonna, The Transfiguration, Vatican Stanze frescoes
4. Sandro Botticelli
A Florentine master celebrated for beauty and flowing linear grace in mythological and religious subjects.
His greatest works blended pagan antiquity with Christian symbolism, creating dreamlike visions that influenced artists for centuries.
- Lifespan: 1445–1510
- Nationality: Italian (Florentine)
- Styles and Themes: Early Renaissance, mythological allegories, linear elegance, religious devotion
- Known For: The Birth of Venus, Primavera, Madonna of the Magnificat, Adoration of the Magi
5. Titian
The master of Venetian color, whose rich, luminous palette and dynamic brushwork changed oil painting. His portraits captured psychological depth while his mythological scenes celebrated sensuality and drama.
- Lifespan: 1488–1576
- Nationality: Italian (Venetian)
- Styles and Themes: Venetian Renaissance, vibrant color, mythological narratives, portraiture
- Known For: Assumption of the Virgin, Venus of Urbino, Bacchus and Ariadne
6. Hans Holbein the Younger
A German-Swiss artist who became court painter to Henry VIII, creating penetrating portraits that revealed character with unflinching honesty.
His precise technique and attention to symbolic detail made him the preeminent portraitist of the Northern Renaissance.
- Lifespan: 1497–1543
- Nationality: German-Swiss
- Styles and Themes: Northern Renaissance, detailed realism, portraiture, religious reform
- Known For: The Ambassadors, portraits of Henry VIII, Dance of Death series, portrait of Thomas More
Baroque and Rococo Artists

The Baroque era introduced dramatic intensity and theatrical lighting to European art. Artists employed bold contrasts and dynamic compositions to get powerful emotional responses and glorify religious authority.
7. Caravaggio
A revolutionary who introduced dramatic chiaroscuro and gritty realism to religious painting, depicting sacred figures as everyday people.
His theatrical lighting and psychological intensity created a visceral emotional impact that changed European art, making him one of the most famous artists in history.
- Lifespan: 1571–1610
- Nationality: Italian (Lombard)
- Styles and Themes: Baroque, tenebrism, dramatic lighting, religious realism, psychological tension
- Known For: The Calling of Saint Matthew, Judith Beheading Holofernes, The Conversion of Saint Paul, Medusa
8. Peter Paul Rubens
A Flemish master whose exuberant, sensuous paintings celebrated life, mythology, and power with dynamic energy. His workshop produced monumental works combining classical learning with Baroque drama.
- Lifespan: 1577–1640
- Nationality: Flemish (Spanish Netherlands)
- Styles and Themes: Baroque, dynamic movement, mythological scenes, robust figures
- Known For: The Descent from the Cross, The Garden of Earthly Delights, Massacre of the Innocents
9. Rembrandt van Rijn
The Dutch master of light and shadow, whose psychological portraits and biblical scenes probed human emotion with unprecedented depth.
His innovative use of impasto and chiaroscuro created intimate, introspective works that revealed inner character.
- Lifespan: 1606–1669
- Nationality: Dutch
- Styles and Themes: Dutch Golden Age, chiaroscuro, psychological depth, self-portraiture
- Known For: The Night Watch, The Jewish Bride, the self-portraits series, The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp
10. Johannes Vermeer
A Delft painter who captured quiet domestic moments with luminous color and precise spatial geometry. His small oeuvre of intimate interior scenes demonstrated mastery of light, creating meditations on everyday life.
- Lifespan: 1632–1675
- Nationality: Dutch
- Styles and Themes: Dutch Golden Age, domestic interiors, natural light, tranquility, spatial harmony
- Known For: Girl with a Pearl Earring, The Milkmaid, View of Delft, The Art of Painting
11. Jean-Honoré Fragonard
A Rococo master whose playful, sensuous paintings epitomized aristocratic leisure and romantic dalliance in pre-revolutionary France.
His virtuosic brushwork and pastel palette created enchanting scenes of love and pleasure.
- Lifespan: 1732–1806
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Rococo, romantic scenes, aristocratic leisure, sensuality,
- Known For: The Swing, The Progress of Love series, The Bolt, Young Girl Reading, The Stolen Kiss
12. François Boucher
He is the Rococo painter whose mythological and pastoral scenes delighted the French aristocracy with their charm and sensuality.
His decorative style and soft color harmonies defined the aesthetic of Louis XV’s court.
- Lifespan: 1703–1770
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Rococo, mythological scenes, pastoral idylls, sensuality, decorative charm
- Known For: The Toilette of Venus, Reclining Girl, Shepherd’s Idyll, Madame de Pompadour portraits
13. Nicolas Poussin
A French painter working in Rome who championed classical order, clarity, and intellectual rigor in art.
His philosophical approach to composition and mythological subjects established him as the father of French classicism.
- Lifespan: 1594–1665
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Classical Baroque, rational composition, mythological narratives
- Known For: Et in Arcadia ego, The Rape of the Sabine Women, The Four Seasons series
Romanticism and Realism
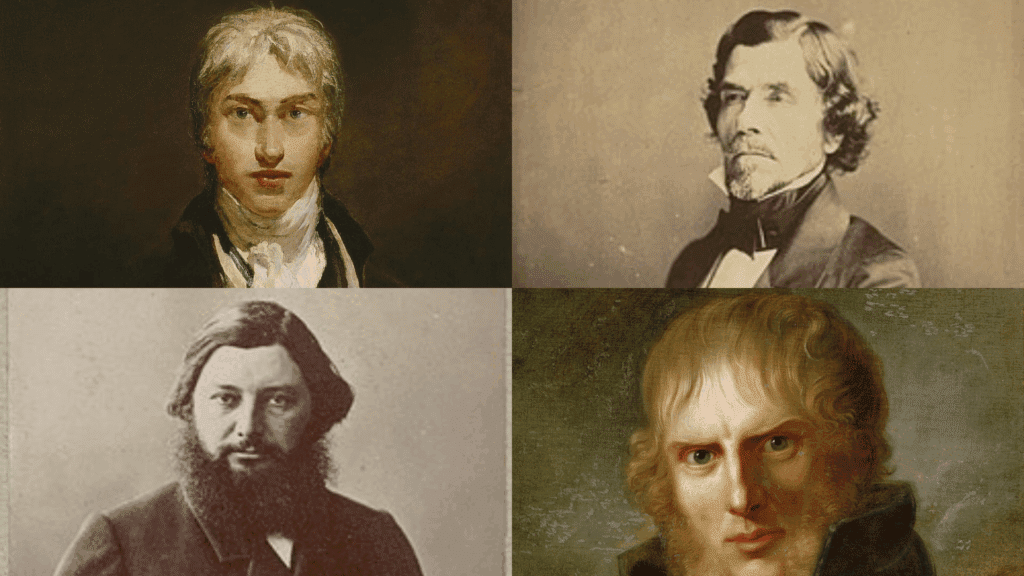
Romanticism lifted emotion and nature’s sublime power over rationality, while Realism rejected idealization to portray ordinary life with unflinching honesty.
These historical artists challenged academic conventions and significantly expanded art’s subject matter.
14. J.M.W. Turner
An English painter who changed landscape art through atmospheric light effects and sublime natural drama. His increasingly abstract seascapes and storms pushed painting toward modernism while seeing nature’s power.
- Lifespan: 1775–1851
- Nationality: British (English)
- Styles and Themes: Romanticism, atmospheric effects, sublime nature, maritime scenes
- Known For: The Fighting Temeraire, Rain, Steam and Speed, The Slave Ship
15. Caspar David Friedrich
A German Romantic who painted contemplative landscapes where solitary figures confronted nature’s infinity and mystery. His symbolic vistas expressed spiritual longing and the sublime experience of the natural world.
- Lifespan: 1774–1840
- Nationality: German
- Styles and Themes: Romanticism, sublime landscapes, spiritual symbolism, solitary contemplation
- Known For: Wanderer Above the Sea of Fog, The Sea of Ice, Abbey in the Oakwood, Chalk Cliffs on Rügen
16. Eugène Delacroix
A French Romantic whose passionate, colorful canvases depicted exotic subjects and revolutionary fervor with dynamic brushwork.
His dramatic compositions and expressive color influenced Impressionism and subsequent modern movements.
- Lifespan: 1798–1863
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Romanticism, dramatic action, exotic Orientalism, political revolution
- Known For: Liberty Leading the People, The Death of Sardanapalus, Women of Algiers
17. Gustave Courbet
A Realist pioneer who rejected idealization to paint ordinary people and everyday life. His bold technique and democratic subject matter challenged academic conventions and influenced social realism.
- Lifespan: 1819–1877
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Realism, working-class subjects, unidealized figures, social commentary
- Known For: The Stone Breakers, A Burial at Ornans, The Artist’s Studio, The Origin of the World
18. Jean-François Millet
A Realist who dignified peasant labor through monumental compositions that lifted rural workers to heroic status.
His sympathetic portrayals of agricultural life combined social consciousness with spiritual reverence for humble toil.
- Lifespan: 1814–1875
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Realism, peasant life, agricultural labor, rural dignity, social awareness
- Known For: The Gleaners, The Angelus, The Sower, Man with a Hoe, Shepherd Tending His Flock
Impressionists and Post-Impressionists

Impressionism revolutionized painting by capturing fleeting moments through broken brushwork and pure color, carried out by the famous artists in history of this era.
Post-Impressionists built upon these innovations while pursuing individual visions, paving the way for modern art’s radical experiments.
19. Claude Monet
Claude Monet is the father of Impressionism, whose serial paintings of light effects on water, haystacks, and cathedrals revolutionized perception itself.
His dedication to capturing fleeting atmospheric moments established plein air painting and modern color theory.
- Lifespan: 1840–1926
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Impressionism, light effects, atmospheric conditions, water reflections
- Known For: Water Lilies series, Impression Sunrise, Rouen Cathedral series, Haystacks series
20. Edgar Degas
He was an Impressionist who preferred indoor subjects, capturing ballet dancers, café scenes, and women at their toilette with unconventional compositions.
His mastery of movement and innovative cropping techniques influenced photography and modern art.
- Lifespan: 1834–1917
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Impressionism, ballet dancers, modern life, movement studies
- Known For: The Ballet Class, L’Absinthe, The Dance Class, Little Dancer Aged Fourteen sculpture
21. Camille Pissarro
A founding Impressionist whose landscapes and rural scenes saw light and atmosphere with scientific rigor. His mentorship of younger artists and exploration of Neo-Impressionism showed constant artistic change.
- Lifespan: 1830–1903
- Nationality: French (born in Danish West Indies)
- Styles and Themes: Impressionism, rural landscapes, urban scenes, light studies
- Known For: Boulevard Montmartre series, The Harvest, The Garden of Pontoise, The Avenue de l’Opéra
22. Vincent van Gogh
A Post-Impressionist whose emotionally charged paintings expressed inner turmoil through vivid color and turbulent brushwork, he is one of the most famous artists of all time.
His passionate intensity and expressive technique profoundly influenced Expressionism and the study of subjective experience in modern art.
- Lifespan: 1853–1890
- Nationality: Dutch
- Styles and Themes: Post-Impressionism, emotional expression, vibrant color, swirling brushwork
- Known For: The Starry Night, Sunflowers series, The Bedroom, Café Terrace at Night, self-portraits, Irises
23. Paul Cézanne
A Post-Impressionist who analyzed form through geometric shapes and constructed space through color planes. His revolutionary approach to structure and perspective laid the foundation for Cubism and abstract art.
- Lifespan: 1839–1906
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Post-Impressionism, geometric forms, spatial structure, still life analysis
- Known For: Mont Sainte-Victoire series, The Card Players, The Bathers, Still Life with Apples
24. Pierre-Auguste Renoir
An Impressionist who celebrated beauty, pleasure, and human warmth through luminous portraits and leisurely scenes.
His soft brushwork and radiant palette captured joy and sensuality in modern Parisian life.
- Lifespan: 1841–1919
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Impressionism, joyful celebration, sensuous figures, leisure activities
- Known For: Dance at Le Moulin de la Galette, Luncheon of the Boating Party, The Umbrellas, Two Sisters
Modern Artist

Modernism shattered traditional representation through radical formal experimentation, embracing abstraction and conceptual innovation.
These most famous artists rejected naturalistic depiction in favor of pure form, color relationships, and subjective expression.
25. Pablo Picasso
A Spanish revolutionary who co-founded Cubism and continuously reinvented artistic language throughout seven decades.
His protean creativity encompassed multiple styles, from Blue Period melancholy to Cubist fragmentation.
- Lifespan: 1881–1973
- Nationality: Spanish
- Styles and Themes: Cubism, multiple perspectives, formal experimentation
- Known For: Les Demoiselles d’Avignon, Guernica, The Old Guitarist, The Weeping Woman
26. Georges Braque
A French painter who co-developed Cubism with Picasso, breaking down objects into geometric facets and multiple viewpoints. His analytical approach and subtle color harmonies laid the intellectual foundation for Cubism.
- Lifespan: 1882–1963
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Cubism, geometric analysis, multiple perspectives, still life deconstruction
- Known For: Houses at L’Estaque, Violin and Candlestick, Man with a Guitar, The Portuguese
27. Henri Matisse
A Fauvist leader whose bold, flat color and simplified forms celebrated pure visual pleasure.
His lifelong study of color relationships and patterns created joyful compositions that balanced emotion with formal grace.
- Lifespan: 1869–1954
- Nationality: French
- Styles and Themes: Fauvism, pure color, decorative patterns, simplified forms, Mediterranean light
- Known For: The Dance, Blue Nude series, Woman with a Hat, The Red Studio, Jazz cutouts
28. Wassily Kandinsky
A Russian pioneer of abstract art who liberated painting from representation to find spiritual dimensions through color and form.
His theoretical writings and compositions established abstraction as a vehicle for inner expression and universal harmony.
- Lifespan: 1866–1944
- Nationality: Russian (naturalized French and German)
- Styles and Themes: Abstract art, spiritual expression, synesthesia, color theory
- Known For: Composition VII, Composition VIII, Yellow-Red-Blue, Several Circles
29. Marc Chagall
A Russian-French artist, he is one of the most famous artists in history, and his dreamlike paintings blended folk imagery, Jewish mysticism, and modernist innovation.
His poetic fantasies and floating figures created worlds where memory, love, and spirituality surpassed logic.
- Lifespan: 1887–1985
- Nationality: Russian-French (Belarusian-born)
- Styles and Themes: Modernism, dreamlike fantasy, Jewish folklore, romantic love, floating figures
- Known For: I and the Village, The Birthday, White Crucifixion, Paris Through the Window
30. Paul Klee
A Swiss-German artist whose playful, symbolic works bridged abstraction and figuration with childlike wonder.
His knowledge of color theory, line, and symbolic language created intimate, contemplative compositions rich with philosophical meaning.
- Lifespan: 1879–1940
- Nationality: Swiss-German
- Styles and Themes: Abstract Expressionism, symbolic imagery, color theory, childlike simplicity
- Known For: Twittering Machine, Castle and Sun, Senecio, Ad Parnassum, Cat and Bird
Surrealists and Expressionists
Surrealism explored unconscious minds through dreamlike imagery, while Expressionism prioritized raw emotional intensity. These famous artists in history dared to venture into psychological depths that previous generations had avoided.
Both movements rejected artistic decorum to see humanity’s darker inner realities.
31. Salvador Dalí
A Spanish Surrealist whose meticulously rendered dreamscapes featured melting clocks, distorted figures, and impossible scenarios.
His theatrical personality and technical virtuosity made him Surrealism’s most recognizable figure. Salvador was always keen on exploring psychoanalytic themes with hallucinatory precision.
- Lifespan: 1904–1989
- Nationality: Spanish (Catalan)
- Styles and Themes: Surrealism, dream imagery, Freudian symbolism, melting forms
- Known For: The Persistence of Memory, The Elephants, Swans Reflecting Elephants
32. René Magritte
A Belgian Surrealist who challenged perception through ordinary objects placed in extraordinary contexts.
His witty, thought-provoking images questioned reality and representation, using precise technique to depict philosophical paradoxes.
- Lifespan: 1898–1967
- Nationality: Belgian
- Styles and Themes: Surrealism, philosophical paradoxes, visual riddles, everyday objects
- Known For: The Treachery of Images, The Son of Man, Golconda, The Lovers, Empire of Light
33. Edvard Munch
A Norwegian Expressionist whose raw psychological intensity captured anxiety, love, and death with disturbing power. His image of existential dread and swirling, emotional compositions profoundly influenced German Expressionism.
- Lifespan: 1863–1944
- Nationality: Norwegian
- Styles and Themes: Expressionism, psychological anxiety, existential dread, love, and death
- Known For: The Scream, The Vampire, Madonna, The Sick Child, Anxiety
34. Egon Schiele
An Austrian Expressionist whose contorted figures and graphic eroticism explored sexuality, mortality, and psychological vulnerability.
His angular line work and raw honesty created disturbing yet compelling portraits of human fragility.
- Lifespan: 1890–1918
- Nationality: Austrian
- Styles and Themes: Expressionism, distorted figures, sexuality, psychological tension, mortality, raw emotion
- Known For: Self-Portrait with Physalis, The Embrace, Portrait of Wally, Seated Woman with Bent Knee
35. Jackson Pollock
An American Abstract Expressionist who revolutionized painting through the drip technique and all-over composition. His energetic, spontaneous method emphasized the physical act of painting.
- Lifespan: 1912–1956
- Nationality: American
- Styles and Themes: Abstract Expressionism, action painting, spontaneous gesture, subconscious expression
- Known For: No. 5, 1948, Autumn Rhythm, Blue Poles, Convergence, Lavender Mist
Contemporary and Street Artists

Contemporary art encompasses a diverse range of media while challenging traditional definitions. Street art democratizes creativity by bringing it into public spaces and engaging with social issues and identity politics.
These contemporary creators continue the legacy of famous artists in history by pushing boundaries and redefining what art means in the modern world.
36. Jean-Michel Basquiat
An American Neo-Expressionist who merged street art energy with the grace of fine arts, addressing race, power, and identity. His raw, text-heavy canvases combined African symbolism and social commentary with explosive color.
- Lifespan: 1960–1988
- Nationality: American
- Styles and Themes: Neo-Expressionism, graffiti influence, racial identity, social commentary
- Known For: Untitled (1982 skull painting), Hollywood Africans, Irony of Negro Policeman
37. Banksy
An anonymous British street artist whose satirical stencils and installations critique consumerism, war, and authority.
His guerrilla art tactics and provocative humor have made political commentary accessible while questioning the values of the art market.
- Lifespan: 1974–present
- Nationality: British (English, presumed)
- Styles and Themes: Street art, political satire, anti-establishment, social critique, dark humor
- Known For: Girl with Balloon, Flower Thrower, Napalm, Love is in the Bin, Dismaland installation
38. Yayoi Kusama
A Japanese artist whose immersive infinity rooms and obsessive polka dot patterns explore infinity, repetition, and psychological states.
Her autobiography changes mental illness into art experiences, combining sculpture, installation, and performance.
- Lifespan: 1929–present
- Nationality: Japanese
- Styles and Themes: Contemporary art, infinity, repetition, polka dots, psychological obsession
- Known For: Infinity Mirror Rooms, pumpkin sculptures, polka dot installations, Narcissus Garden
39. Damien Hirst
A British artist who dominates contemporary art through conceptual works examining death, desire.
His provocative use of preserved animals, diamond-encrusted skulls, and pharmaceutical imagery challenges artistic value while achieving commercial success.
- Lifespan: 1965–present
- Nationality: British (English)
- Styles and Themes: Contemporary conceptual art, mortality, consumerism, scientific imagery
- Known For: The Physical Impossibility of Death in the Mind of Someone Living (shark)
40. Shepard Fairey
An American street artist and graphic designer whose politically charged posters blend propaganda vibes with contemporary activism.
His iconic Obama “Hope” poster and OBEY Giant campaign changed street art into powerful tools for social commentary and political engagement, securing his place among famous artists in history who used art for social change.
- Lifespan: 1970–present
- Nationality: American
- Styles and Themes: Street art, political activism, propaganda aesthetics, social commentary, graphic design
- Known For: Obama “Hope” poster, OBEY Giant campaign, Andre the Giant Has a Posse
41. Jenny Holzer
An American conceptual artist who uses text-based installations to confront viewers with provocative truths about power, violence, and society.
Her LED displays and projected messages in public spaces challenge conventional art presentation while addressing urgent social and political issues.
- Lifespan: 1950–present
- Nationality: American
- Styles and Themes: Conceptual art, text-based installations, public intervention, political commentary
- Known For: Truisms series, Inflammatory Essays, LED installations, Xenon projections, Lustmord series
Wrapping It Up
The famous artists profiled here shaped humanity’s creative vision across the centuries, from Renaissance innovation to contemporary experimentation.
If you’re drawn to Monet’s luminous gardens, Picasso’s cubist revolution, or Banksy’s provocative street art, each historical artist offers different insights into their era and the human condition.
Understanding these historical artists deepens our appreciation for how creativity shapes culture and human expression. From classical paintings to digital art displayed on screens, their influence remains undeniable.
Start learning about their masterpieces. Your path through art history can start with a single painting.